You’ve likely heard it before: “All businesses are now digital businesses.” But since the business has expanded into digital space, shouldn’t something as critical as business security digitally expand too? That’s where the VMware ubiquitous software layer comes into play — sitting across the application infrastructure and endpoints, no matter where they are.
Now more than ever, it’s clear that security expertise is a must-have for IT. To further enhance your own security knowledge, make sure to join us at vForum Online on June 28th — right from your own desk. As our largest virtual conference, vForum Online is a must-attend event for IT professionals, and especially for those looking to improve their approach to security.
For returning attendees, you may notice we’ve made some alterations to the structure of vForum Online: Now, the conference is divided into several goal-oriented tracks, to ensure we’re aligned to your IT aims.
With this free, half-day event just a few weeks away, we’re counting down the days — and counting up all the reasons you should attend. Get a preview of these five security spotlights you can expect at the conference:
- A Modern Approach to IT Security
In our “Transform Security — Reduce Risk, Increase Agility, and Control CapEx” breakout session, we’ll walk you through the benefits of the VMware ubiquitous software layer for security: how it secures application infrastructure, identity, and endpoints, and also streamlines compliance in an increasingly hybrid and complex IT environment.
Still have questions? In a Chat with Experts, you’ll talk live with a seasoned security pro to get the answers you need.
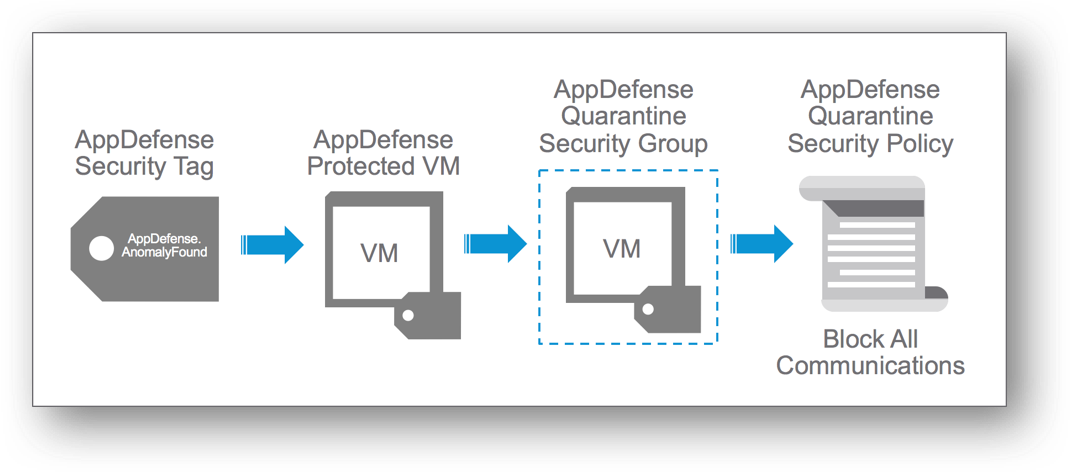
- All About Micro-segmentation
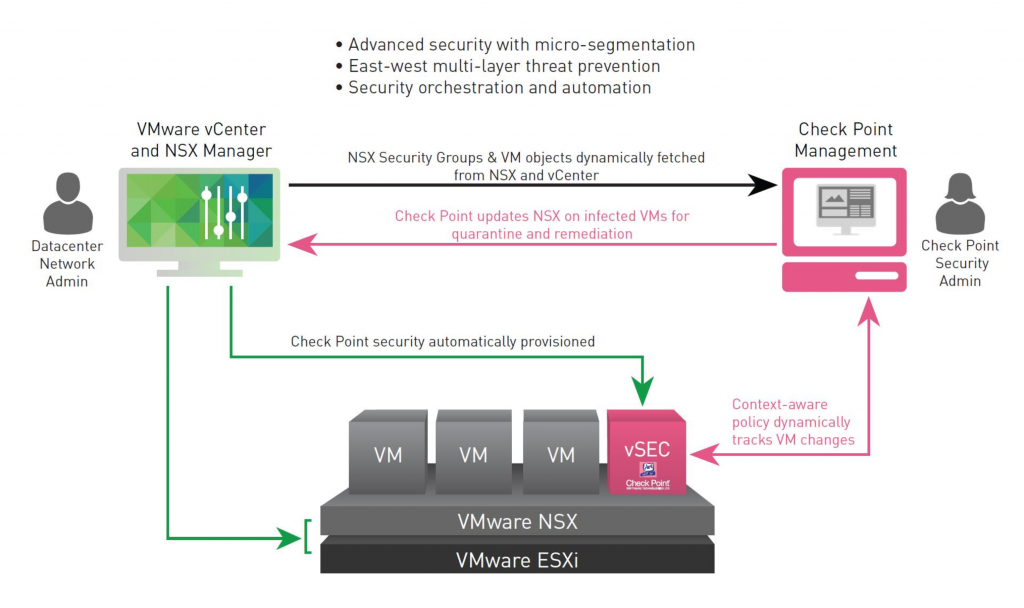
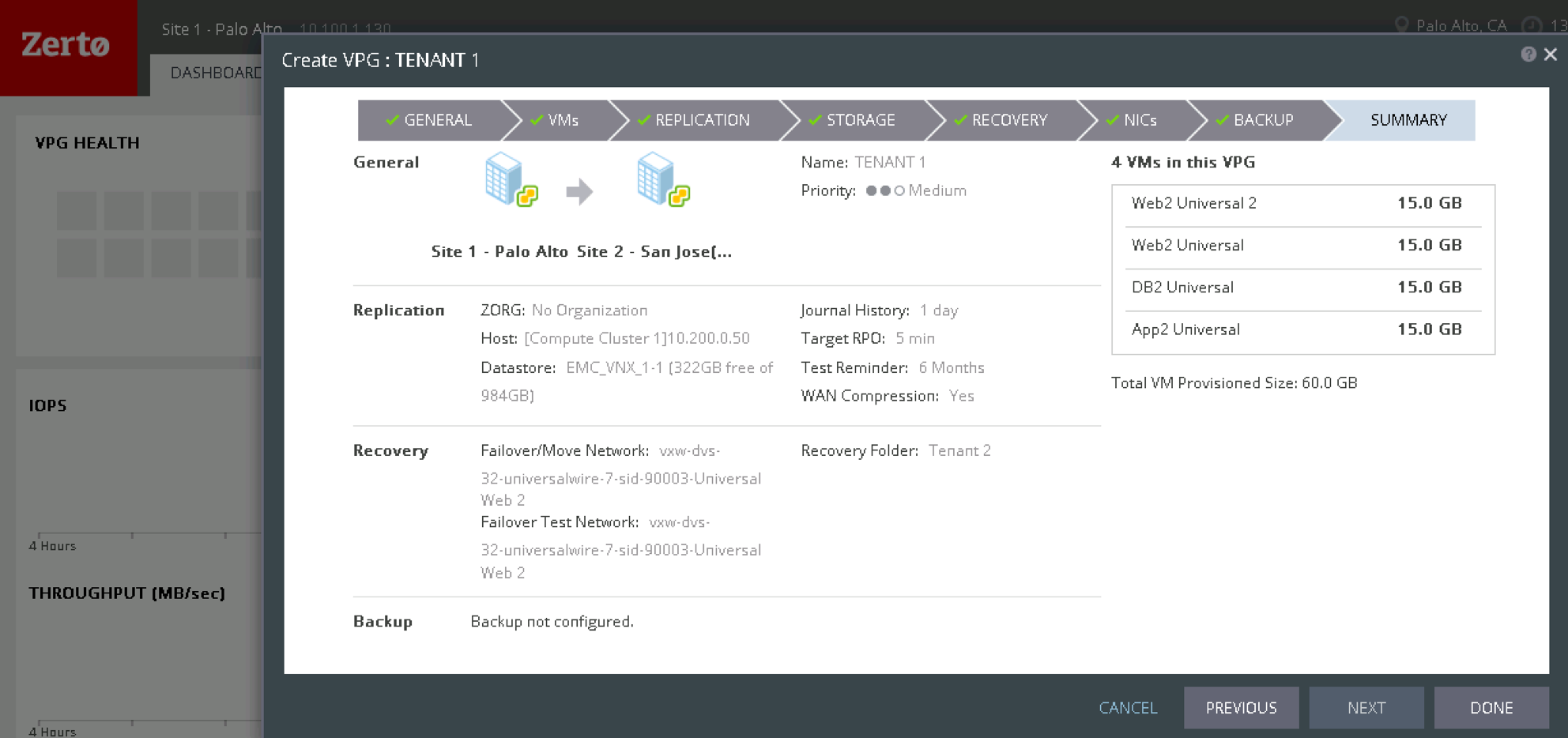
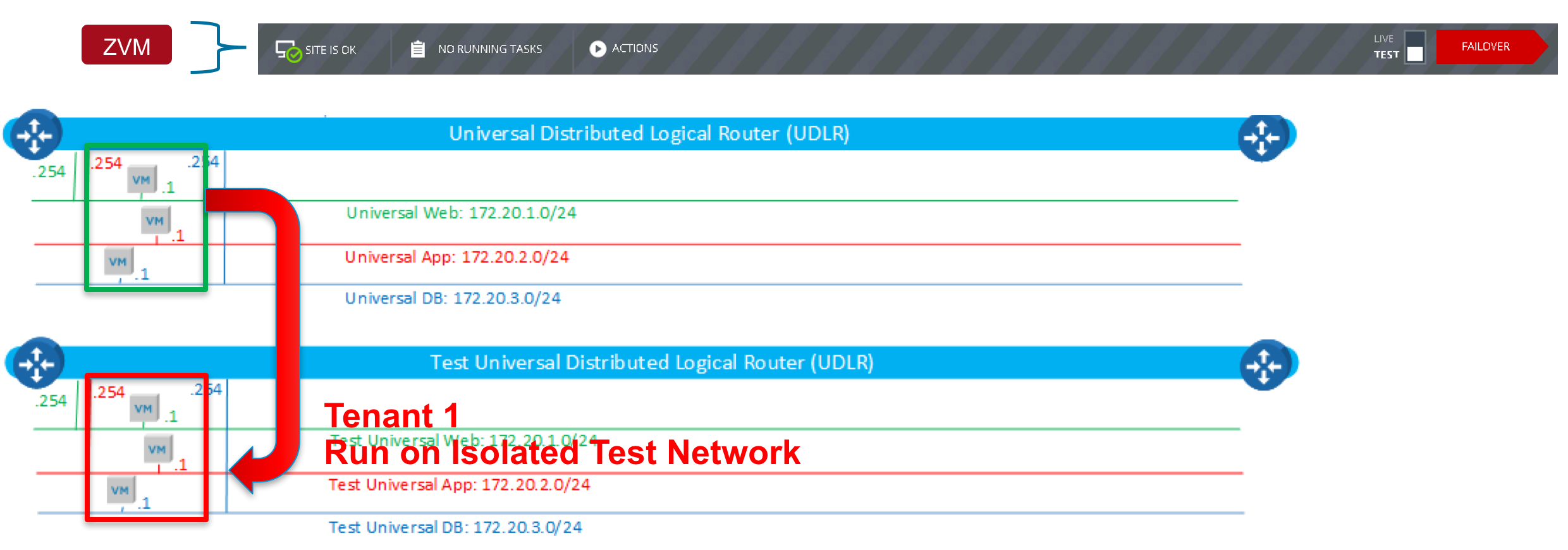
Thanks to software Micro-segmentation, IT is able to simplify security policies and align them to the applications themselves. Micro-segmentation enables IT to define security policies at the individual VM level, so that as workloads move between public and private clouds throughout their lifecycles, their security policies move with them.
You’ll be able to take a closer look at Micro-segmentation in our “Secure Application Infrastructure — Micro-segmentation Technology Deep-Dive” breakout session. Then, you can ask for individualized support in the Micro-segmentation-themed “Chat with Experts.”
- Dig Into Defense-in-Depth Security
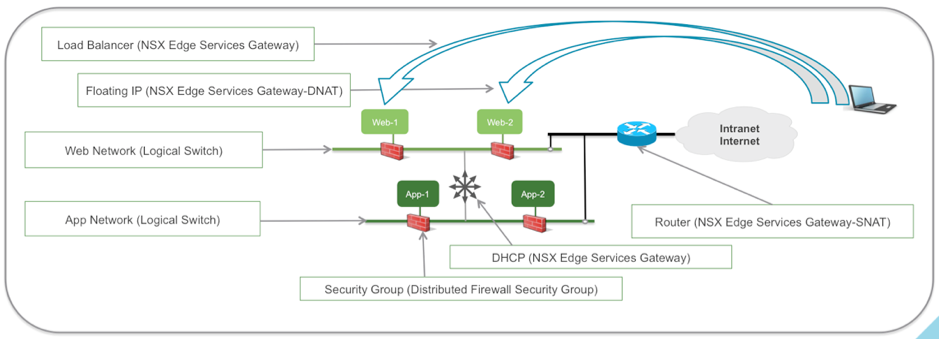
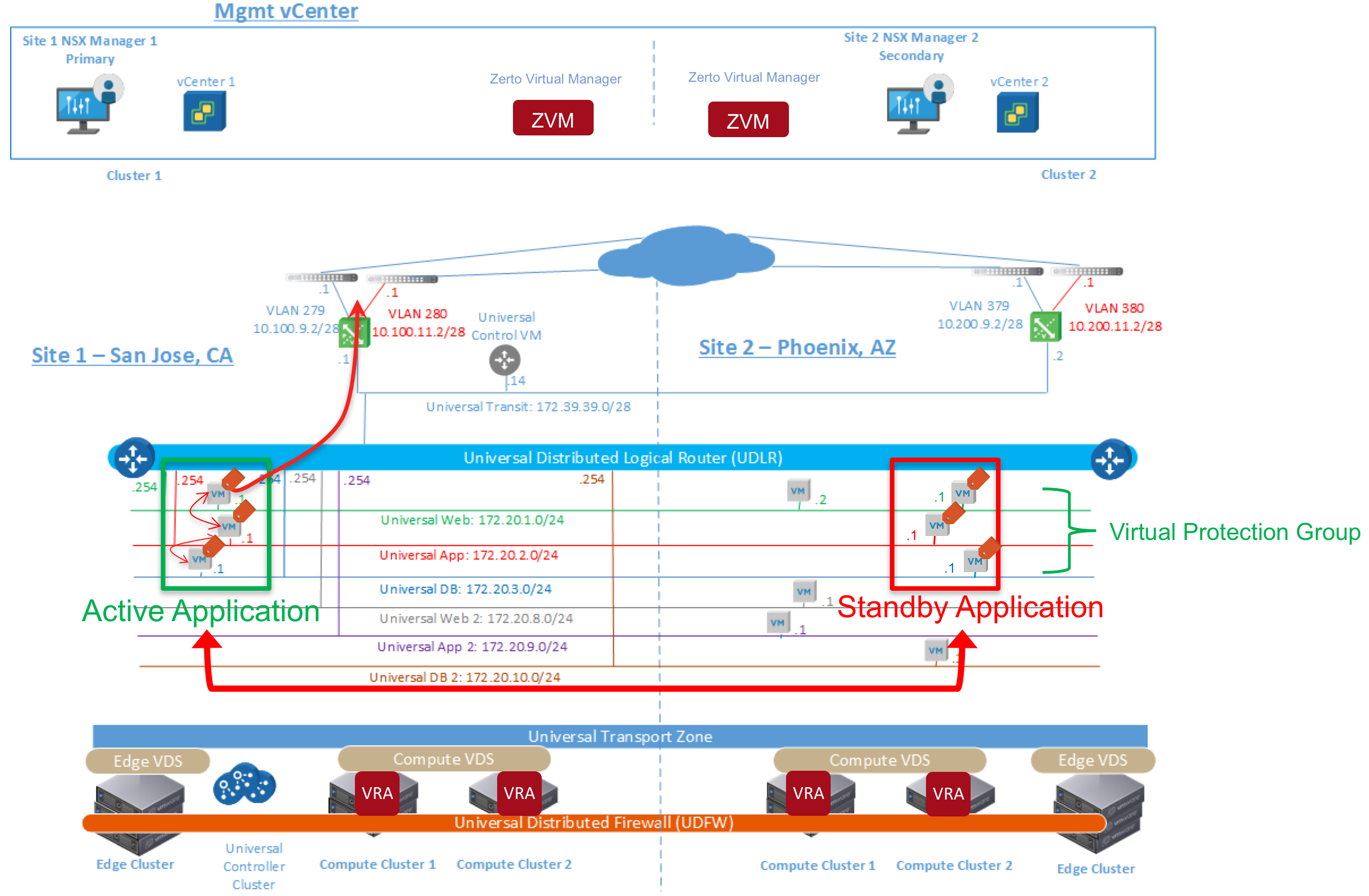
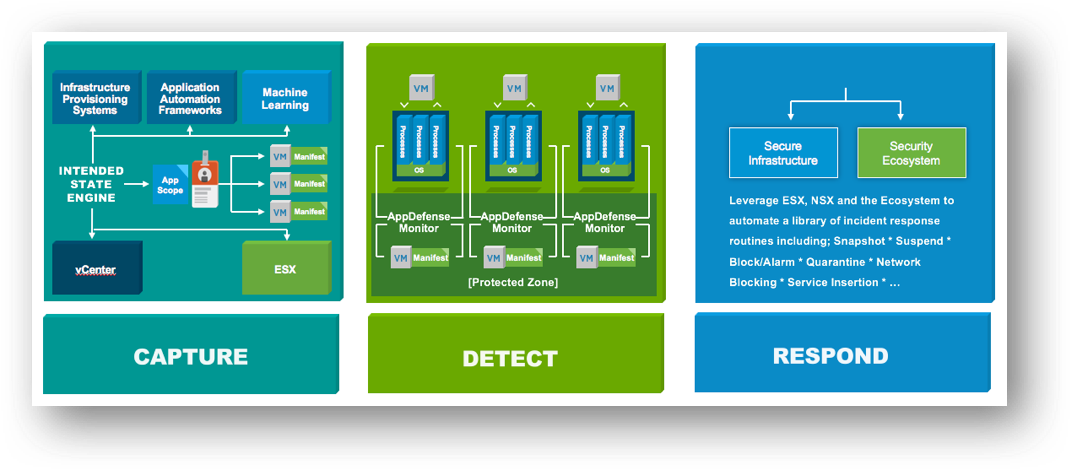
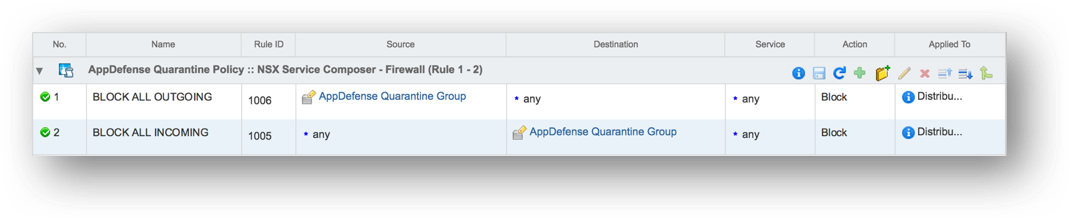
Want to peek at some of the advantages of security in Software-Defined Data Center? Start with our breakout session, “Design Defense-in-Depth Security in the Software-Defined Data Center Using vSphere v6.5 and NSX 6.3,” where you’ll become acquainted with the features of specific solutions like VMware NSX® 6.3 and VMware vSphere v6.5®.
A Software-Defined Data Center Specialist will be on hand to help you dig deeper into the topic (and design your own defense-in-depth security approach) — in one of our Chats with Experts.
- Customer Success Story on Security
Learn something new from one of your peers. In our “Customer Story” breakout session, we’ll review a real security success story from a VMware customer, the Deluxe Corporation. You’ll see specifically how this business was able to achieve superior security with a ubiquitous software layer across their application infrastructure and endpoints. The result? Maximized visibility, content, and control — to secure interactions between all users, applications, and data. With the insights you’ll gain in this session, you’ll begin to innovate on your own security.
- NSX Hands-on Labs
Want to know what we’re most looking forward to at the June 28th vForum? The Hands-on Labs. In two security-focused demos, you’ll get interactive as you explore NSX and its many features. You can also join a Lab specifically on distributed firewall and Micro-segmentation with NSX. Sign up for a single one, or do double duty. Your choice.
And by the way, there will be a few other special bonuses on the big day. It all kicks off with an opening keynote from our CEO, Pat Gelsinger. In his talk, “5 Myths of IT,” Pat will bust some common IT myths and share his perspective on IT today.
Throughout the day, we’ll also be giving away awesome prizes, like an Oculus Rift VR headset and a voice-controlled Amazon Echo speaker. So, come join us for the learning — and stay for a prize.
Register for vForum Online on June 28. We look forward to your attendance.
The post Don’t Miss out on These 5 Spotlights on Security at vForum Online Summer 2017 appeared first on Network Virtualization.